Sri Lanka is deeply troubled about the death of over hundred people who were waiting to receive aid in Gaza and joins the call for investigation into the incident.
The latest incident underscores the immediate need to end the blockade imposed on Gaza, depriving its civilian population, including women and children, of access to basic necessities such as food, water, medicine, electricity, and fuel.
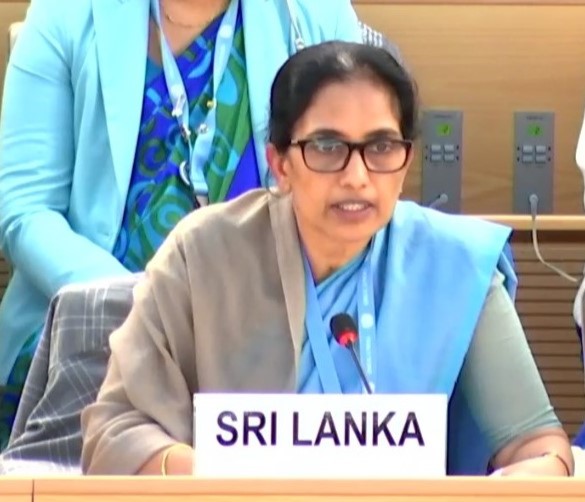

Statement by Her Excellency Himalee Arunatilaka, Ambassador and Permanent Representative of Sri Lanka to the United Nations in Geneva at the
55th Session of the United Nations Human Rights Council
(as the country concerned following the Oral Update on Sri Lanka
by the High Commissioner for Human Rights)
01 March 2024
Mr. President,
The Hon. Minister of Foreign Affairs of Sri Lanka, in his address to this Council earlier this week, highlighted that Sri Lanka has over the years engaged actively and constructively with this Council. He also elaborated on our recent engagements with a number of working methods of the Council. It is in this context that I take the floor today, specifically to provide more details on the progress made on matters of relevance to this Council.
Mr. President,
Excellencies,
Distinguished delegates,
Ladies and gentlemen,
Let me begin, Mr. President, by congratulating you on your election as the President of the Council. I assure you of my delegation’s full cooperation in discharging your duties.
Sri Lanka has over the years, engaged actively and constructively with the UN Human Rights Council, to enhance the multilateral framework for the promotion and protection of human rights.
Despite the severe constraints we faced, particularly in the recent past, we have continued to maintain such engagement with an extensive array of the helpful working methods of this Council that we believe are productive and beneficial to our people. Our recent engagements, including the UPR Review under the 4th Cycle in February 2023 and the ICCPR Review in March 2023, reflect our commitment to constructive dialogue on human rights and reconciliation.

Mr. President
Madam Secretary-General of the Conference on Disarmament
Excellencies
Ladies and Gentlemen
I extend my felicitations to you Mr. President on assuming the Presidency of this Conference and assure you of my country’s fullest support in carrying out the important work of this Conference.
I also appreciate the commitment and the untiring efforts of the Indian presidency that preceded, towards building consensus through open and broad consultations.
I am addressing this important body at a decisive time in human history. The need is more vital than ever, for effective disarmament diplomacy.



Conference on Disarmament: Plenary meeting – Tuesday, 30 January 2024
Statement by Sri Lanka
Mr. President
On behalf of the Sri Lanka delegation, it is my pleasure to congratulate Ambassador Ray of India on assuming the first presidency of the Conference on Disarmament for the 2024 session.
- Message by H.E. the President of Sri Lanka on the International Day of Solidarity with the Palestinian People, 29 November 2023
- Anti-Personnel Mine Ban Convention (APMBC), Twenty-First Meeting of State Parties, 20-24 November 2023, Statement by Sri Lanka – Agenda Item 10 a – Assisting the Victims
- Anti-Personnel Mine Ban Convention (APMBC), Twenty-First Meeting of State Parties, 20-24 November 2023, Statement by Sri Lanka-General Exchange of Views

